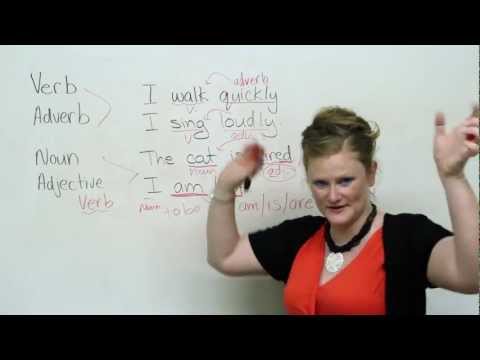They are adverbs of time, adverbs of place, adverbs of degree and adverbs of manner. Adverbs of time talk about the time factor related to the verb. Some examples for adverbs of time are now, never, often, etc. Adverbs of place speak about the venue related to the verb. Some examples are here, there, everywhere, etc. Adverbs of degree speak about the extent to which some action was done.
Partly, almost and fully are some such examples. Adverbs of manner tell in what way an action was performed. Slowly, fast, deliberately are some examples for that. Because "feel" is a verb, it seems to call for an adverb rather than an adjective. But "feel" isn't just any verb; it's a linking verb. An adverb would describe how you perform the action of feeling—an adjective describes what you feel.
"I feel badly" means that you are bad at feeling things. Like adjectives, adverbs can show degrees of comparison, although it's slightly less common to use them this way. With certain "flat adverbs" , the comparative and superlative forms look the same as the adjective comparative and superlative forms. It's usually better to use stronger adverbs rather than relying on comparative and superlative adverbs.
Adverbs are words that describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Adverbs give us more information about how something is being done or the degree to which something is true. Adverbs often end with -ly, but there are common adverbs that don't end in -ly . There are also words that end in -ly but aren't adverbs . The auxiliary verbs, such as 'have', 'be' and 'do' have their negative forms in 'n't' as do many modal verbs, such as 'should', 'could' and 'might'. However, the negative forms of these verbs when using contractions are not always created by simply adding 'n't'.
Verb and Adverb show multiple differences between them as they are two different parts of speech. Verb and adverb, as parts of speech, should be understood with the difference between them. Verb and adverb, each does two different tasks in the language. In the meantime, adverb modifies the verb. But in fact, despite the similarity of their names, verbs and adverbs have two different jobs. The main difference between verbs vs. adverbs is that verbs are action words, and adverbs are description words.
Verbs state the action performed by a noun, while adverbs provide more information about how that action is performed. Some adverbs can modify entire sentences—unsurprisingly, these are called sentence adverbs. Common ones include generally, fortunately, interestingly, and accordingly. Sentence adverbs don't describe one particular thing in the sentence—instead, they describe a general feeling about all of the information in the sentence. The adverbs in each of the sentences above answer the question in what manner?
Adverbs can answer other types of questions about how an action was performed. They can also tell you when and where . • There are adverbs of time, adverbs of place, adverbs of manner and adverbs of degree.
The above sentences are a mix of physical actions, mental actions, and state of being. The verbs in the first two sentences ran and ate are examples for physical action. These are actions that we do using our physical body. Then, in the third and fourth sentences, we have the verbs thought and consider.
Thought and consider are examples for mental action. These are actions that we perform using our mind. If is not visible as running to the store.
Then, we have the verbs was and is in the fifth and sixth sentences. Was and is are examples for state of being. These words describe the status of a person at the time of speaking. These state of being verbs are the hardest to spot though they are the ones that are used the most.
Ernest Hemingway is often held up as an example of a great writer who detested adverbs and advised other writers to avoid them. In reality, it's impossible to avoid adverbs altogether. Sometimes we need them, and all writers use them occasionally.
The trick is to avoid unnecessary adverbs. Most of the time, you'll come up with a better word and your writing will be stronger for it. The lexical verb class is an open class of verbs that contains all verbs apart from the auxiliary verbs. The lexical verbs are the main verb vocabulary of a language, telling us the action that is happening in a sentence. There is another interesting fact about adverbs.
Though adverbs primarily modify verbs, adverbs also modify adjectives and other adverbs in sentences. Adverbs can also modify adjectives and other adverbs. Often, the purpose of the adverb is to add a degree of intensity to the adjective. Hi Sid, you could check out our various language learning tips in the Students tab of the main menu for ideas. One important tip for memorising new vocabulary is to put the new words into context. Build meaningful sentences using the vocabulary and revisit the words regularly.
Verbs and adverbs are some of the most exciting parts of language because they relate to action. In the first sentence, the word ugly is the adjective that describes the noun Samantha. The word horridly that modifies this adjective by intensifying its meaning is an adverb.
So, here, the adverb horridly modifies an adjective. In the second sentence, the world well is the adverb that modifies the verb complete. The word remarkably intensifies the meaning of the adverb well. So, in this example, the adverb remarkably modifies another adverb, which is well.
We hope this article has helped clear up any confusion in the verbs vs. adverbs debate! If you encounter anyone else wondering, What are verbs and adverbs? At one time, the use of the word hopefully as a sentence adverb (e.g., Hopefully, I'll get this job) was condemned. People continued to use it though, and many style guides and dictionaries now accept it. There are still plenty of readers out there who hate it though, so it's a good idea to avoid using it in formal writing.
What Is A Verb And Adverb With Examples Adverbs add more information about the action . The adverbs in a sentence are often obvious from their 'ly' ending. A sentence will usually contain verbs together with nouns, while adding adverbs makes writing more interesting and gives it character. A verb is a part of speech that denotes action. In a sentence, usually a verb talks about the action the subject performs. A verb can express a physical action, a mental action, as well as a state of being.
Let us understand these uses with some examples. Elite Editing providesprofessional proofreading, editing, and writing services for students, writers, businesses, ESL, academics, website creators, and others. Some of the most common adverbs are the trickiest because they're irregular.
Good and well, for example, are frequently confused, as are bad and badly. The best business adverbs are the ones you don't use. Instead of using a verb plus an adverb, look for a more precise verb.
A linking verb shows a state of being rather than an action. Instead of the subject of a sentence doing something, a linking verb shows what the subject of a sentence is. The most common linking verbs are to be, to seem, and to become. Of all types of verbs, action verbs are the most powerful.
Action verbs show the performance of an action. They are what the subject of a sentence does. You need them to make a complete sentence—because a subject plus a verb can make a complete thought. And remember that adverbs can be used to modify adjectives as well as verbs and other adverbs. Adverbs tell us how, when, where, and to what degree something happens.
In this way, they modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. Adverbs are inflected for reasons of comparison, by adding 'er', 'est' and also when describing an action we often add 'ly'. Usually, we add 'ly' to the adjective stem to create the adverb. Notice that when you use modal auxiliary verbs, you don't need to use the word 'to' before the verb stem. Verbs and adverbs are integral parts of any language. You can often recognise these words because they usually have the word 'to' preceding them.
A main verb isn't exactly a new category of verb because what makes a verb a main verb is its position and function in a sentence. The main verb is the operative verb in the central clause of a sentence or the verb that's left once all the helping verbs are gone. For example, in this sentence, the main verb is sell. The most common helping verbs are the various forms of be, do, and have, but the remaining helping verbs are equally useful.
We use helping verbs to change the tense or the emphasis of a verb—or both. An adverb is a word that modifies a verb , an adjective , another adverb , or even a whole sentence . Adverbs often end in -ly, but some look exactly the same as their adjective counterparts. Another type of adverb that has a noun derivation are words ending in the suffix 'wards', such as 'homewards'. For example, 'they headed homewards', which means they headed towards home. The suffix 'wards' always indicates direction.
Some English verbs are irregular in their negation in the contracted form, such as the word 'will', which needs the irregular negative inflection 'won't'. Another example is the word 'shall', which needs 'shan't'. Regular verbs have only one form the past tense, the stem plus the 'ed' ending. For example, the verb 'to walk' changes to 'walked' in the past.
English verb inflections include any endings added to the base form of the verb, including 's', 'ing', and 'ed'. The verb inflections of English are really quite simple. In this way, adverbs work in a similar way toadjectives, bringing more interest to the sentence. Adverbs are words that add more detail and describe verbs. Common English adverbs include 'quickly', 'slowly', 'cleverly', 'carefully', 'greedily'. Other adverbs might be confusing because the adjective and adverb are the same word, like fast, late, and early.
The best business writing is often the simplest and most direct—the ideal is to use the fewest possible words to say exactly what you mean. Intransitive verbs, logically enough, don't take an object. They might be qualified with an adverb or two.
There might be a prepositional phrase following the verb. But you can never nap something directly. You can only nap for six hours or nap on the couch or nap soundly. Though the words "adverb" and "verb" sound similar, keep in mind that they are two totally different things. A verb is an action; an adverb is a descriptive word, NEVER an action. It might help to contrast adverbs with adjectives, too.
However, some English adjectives do not change in the adverb form. For example, 'fast' and 'hard' remain the same when used as an adverb. Eventually, English speakers dropped the 'woll' and 'will' became the favoured word for the present tense. However, the 'woll not' (or 'won't' in its contracted form) stayed in the language as the favoured negation of the verb. Sometimes, however, the spelling changes.
For example, often the ending 'e' is omitted when the inflection is added. For example, this happens with the verb 'to make' and the inflected verb 'making'. Verbs are the action words of a sentence. The verbs of the English language can be used in a sentence in many different ways, depending on who or what they are referring to. • There are verbs that talk about physical actions, mental actions and state of being.